What is resonance structure in organic chemistry. In chemistry resonance also called mesomerism is a way of describing bonding in certain molecules or ions by the combination of several contributing structures or forms also variously known as resonance structures or canonical structures into a resonance hybrid or hybrid structure in valence.

What Is Resonance Effect With Example Chemistry Notes Structural Formula Chemistry
Resonance is a key component of valence bond theory and arises when no.

. This and more is covered in the video below. Resonance structures are a useful way of visualizing and representing the bonding in a molecule - they dont actually exist but they are a useful tool to see what the bonding and structure of a compound is. Often they are showed with dotted lines or two structures with an arrow between them.
Resonance structures are significant because they provide a much more. Dont just memorize these arrows move here. Two structures of a given molecule in which the components are the same but the electron placements differ are said to be resonance structures of one another.
What are Resonance Structures When switching from general to organic chemistry showing molecules as structures rather than simple formulas become one of the first things and priorities you need to learn. Identify major and minor resonance contributors. Explain the need for resonance theory.
Resonance is a part of valence bond theory which is used to describe delocalised electron systems in terms of contributing structures each only involving 2-centre-2-electron bonds. Resonance in chemistry is a tool used predominately in organic chemistry to represent certain types of molecular structures. A resonance structure has delocalized electrons Explanation.
Resonance structures are various forms of the same molecule where the electrons have transferred from one region to another. The discussion of resonance effect heavily relies on the understanding of resonance structures. The resonance effect refers to how an electron lone pair interacts with a pi bond to form polarity in a molecule.
Organic Chemistry Resonance What is Resonance. Here we will focus on how to draw resonance structures or resonance contributors for organic. Lewis structures are essential for this as they show all the bonds and electrons in the molecule.
Instead make sure you get why molecules resonate to delocalize their electrons and understand the difference between resonance hybrid and resonance intermediates. In chemistry terms resonance describes the fact that electrons are delocalized or flow freely through the molecule which allows multiple structures to be possible for a given molecule. Sulfur dioxide or SO2 has two resonance structures which contribute equally to the overall hybrid structure of the molecule.
Formal Charge and Oxidation Numbers. Contributing structures of the carbonate ion. What is resonance effect in chemistry.
Meaning the different possible structures for the same molecule with the lowest formal charges distributed differently. Polarisability of Anions The Polarizing Power of Cations. Each individual Lewis structure is called a contributing structure of.
Resonance in chemistry refers to contexts in which one or more electrons contribute to more than one bond in a molecule and are not considered local to any one of the bonds they contribute to. A most common example is found in the resonant bonds between the carbon atoms of benzene rings. Resonance stabilization effect also known as resonance effect as briefly mentioned in Section 13 is one of the fundamental concepts of Organic Chemistry and has broad applications.
Bonding in a compound can sometimes be nicely represented using two-center two-electron bonds - for example methane. Draw the resonance hybrid for a structure. Draw valid resonance structures.
Explain what is a resonance structure and what is not. Resonance structures have two or more possible electron structures. Each contributing resonance structure can be visualized by drawing a Lewis structure.
Why are resonance structures important. Bond Lengths Energies. Properly use curved arrow notation.
A complex Lewis structure is referred to as resonance. Understanding resonance in chemistry helps in figuring out the stability and energy states of a compound. A resonance structure is when there are different forms of a molecule where all formal charges and bonds are the same but they are distributed around the structure differently.
Resonance is a method of describing the delocalized electrons in some molecules where the bonding cannot be explicitly expressed by a single Lewis structure. However a third Lewis structure can be drawn for SO2 which is more stable in theory but doesnt quite match. Also it occurs through the interaction of two pi bonds in adjacent atoms.
Forces and Liquid Structure. Click cc on bottom right for video transcription. However it is important to note that each of these structures cannot actually be observed in nature.
It is a concept that is very often taught badly and misinterpreted by students.

Resonance Structure Easy Science Study Skills Science Chemistry Structure Definition
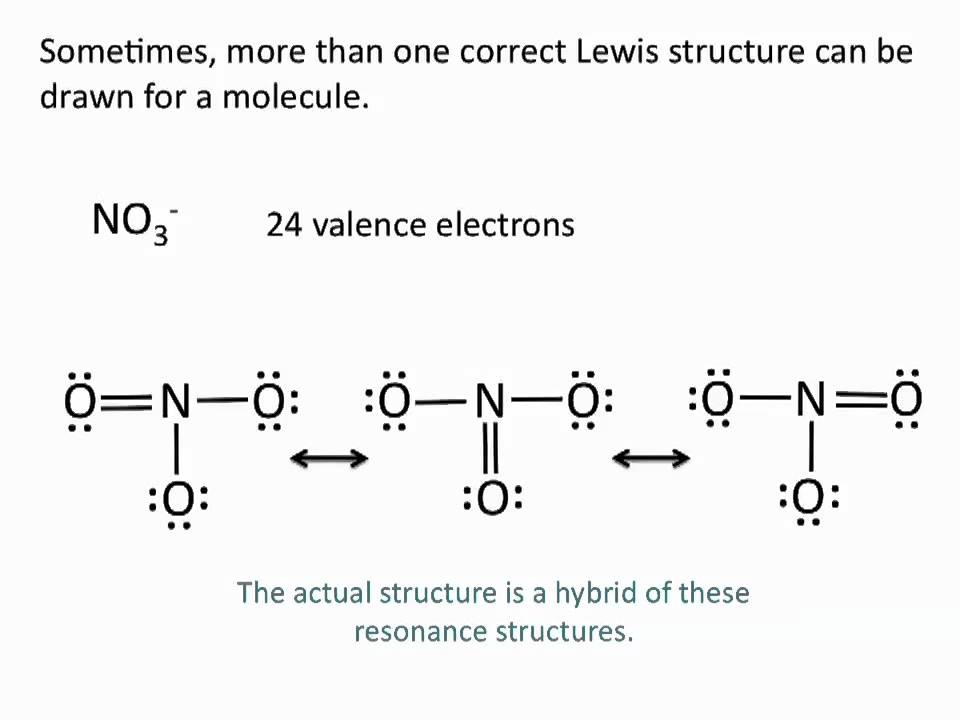
Drawing Lewis Structures Resonance Structures Chemistry Tutorial Youtube Chemistry Science Education Organic Chemistry

Resonance Structures 4 Rules On How To Evaluate Them With Practice Organic Chemistry Chemistry Help Chemistry Worksheets
0 Comments